4204d4
🐳 Docker – Commandes de base

Introduction
Après avoir installé Docker, nous aurons accès à la commande ‘docker’ à partir du ‘shell’ du système d’exploitation du poste de l’installation.
Cette commande nous permettra de gérer l’ensemble des ressources disponibles sous Docker.
Si Docker est installé sur une machine distante, par exemple un serveur Linux, il sera possible d’y avoir accès suite à une connexion ‘ssh’ à partir d’un terminal ou en utilisant l’extension ‘ssh’ de VS Code.
Ouvrir un terminal vers la station possédant une installation de Docker.
$ ssh username@adresse_ip <mot de passe ou clé tls>
# Sous Code, utiliser l'option: Open a remote window.
1.0 – Accès à l’aide intégrée : docker --help
$ docker --help
Usage: docker [OPTIONS] COMMAND
Options:
--config string Location of client config files (default "/Users/alain/.docker")
-c, --context string Name of the context to use to connect to the daemon (...)
-D, --debug Enable debug mode
...
Management Commands:
container Manage containers
image Manage images
...
Commands:
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
build Build an image from a Dockerfile
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
events Get real time events from the server
exec Run a command in a running container
...
💡Note : Sous Linux, si vous obtenez un message de permission refusée :
# Exemple d'erreur:
$ docker run hello-world
docker: Got permission denied while trying to connect to the Docker daemon socket at unix:///var/run/docker.sock: Post http://%2Fvar%2Frun%2Fdocker.sock/v1.40/containers/create: dial unix /var/run/docker.sock: connect: permission denied.
See 'docker run --help'.
---
Solution:
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
sudo chmod 666 /var/run/docker.sock
1.1 – Aide sur une commande spécifique : docker <cmd> --help
Exemple : docker ps --help
docker ps --help
Usage: docker ps [OPTIONS]
List containers
Options:
-a, --all Show all containers (default shows just running)
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print containers using a Go template
-n, --last int Show n last created containers (includes all states) (default -1)
-l, --latest Show the latest created container (includes all states)
--no-trunc Don't truncate output
-q, --quiet Only display container IDs
-s, --size Display total file sizes
👉 Action – Afficher l’aide de la commande ‘run’
❓Question – À quoi servent les options -i -t et -d ?
💡Problème possible avec la console interactive (-it) sous git-bash
https://willi.am/blog/2016/08/08/docker-for-windows-interactive-sessions-in-mintty-git-bash/
Solution :
$ winpty docker exec -it alpine sh
2.0 – Types de commandes Docker Engine
Docker Engine propose deux types de commandes :
- Commandes de gestion (ex:
docker container ls) - Commandes directes (ex:
docker ps)
2.1 – Obtenir l’aide d’une commande de gestion : docker cmdGestion --help
Exemple : docker container --help
$ docker container --help
Usage: docker container COMMAND
Manage containers
Commands:
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
exec Run a command in a running container
ls List containers
rm Remove one or more containers
run Run a command in a new container
start Start one or more stopped containers
...
Run 'docker container COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
** 2.1.1 - Action – Exécuter les commandes suivantes :**
$ docker run hello-world
$ docker run alpine
$ docker run -it -d alpine
# Attention, -it et -d sont des paramètres de 'run', ils ne peuvent pas être placés ailleurs dans l'expression.
Note : ‘alpine’ est une image populaire servant de base à une image personnalisée en raison de sa très petite taille.
2.2 – Obtenir la liste des images locales : docker images
$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
alpine latest 7731472c3f2a 10 days ago 5.61MB
hello-world latest bf756fb1ae65 12 months ago 13.3kB
2.3 – Obtenir la liste des conteneurs en exécution : docker ps
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
c8026675b9b7 alpine "/bin/sh" 48 minutes ago Up 48 minutes intelligent_noether
2.4 – Obtenir la liste de tous les conteneurs – incluant ceux qui sont terminés : docker ps -a
$ docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
c8026675b9b7 alpine "/bin/sh" 49 minutes ago Up 49 minutes intelligent_noether
b321afb1ea0f alpine "-it -d" 49 minutes ago Created practical_lamarr
1114bbe1af61 alpine "/bin/sh" 49 minutes ago Exited (0) 49 minutes ago dazzling_zhukovsky
d09c5b00adca hello-world "/hello" 50 minutes ago Exited (0) 50 minutes ago charming_mcnulty
2.4.1 – Rechercher des images disponibles sur ‘docker hub’ : docker search <expression>
Exemple : docker search cowsay
$ docker search cowsay
NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED
lherrera/cowsay 4
grycap/cowsay Alpine-less Cowsay (with Fortune) 2 [OK]
...
$ docker search alainboudreault
NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL
alainboudreault/phpweb Roule un petit script php qui identifie le h… 0
alainboudreault/superminou 0
alainboudreault/docker-hub-github Lorem ipsum ... 0
alainboudreault/420-4d4-mercredi Premier pas avec hub.docker.com 0
alainboudreault/labo-01 semaine 02 0
alainboudreault/bonjour420 0
alainboudreault/momo-dit Exemple d'utilisation de variables d'environ… 0
alainboudreault/unserveurweb Mon premier test push avec docker-hub 0
...
2.4.2 – Obtenir une image à partir d’un dépôt : docker pull éditeur/image
Exemple : docker pull lherrera/cowsay
$ docker pull lherrera/cowsay
Using default tag: latest
latest: Pulling from lherrera/cowsay
...
Status: Downloaded newer image for lherrera/cowsay:latest
# Afficher les images locales
$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
alpine latest 7731472c3f2a 10 days ago 5.61MB
hello-world latest bf756fb1ae65 12 months ago 13.3kB
lherrera/cowsay latest 47e12946765b 4 years ago 186MB
Note : Lorsque nous téléchargeons une image, nous obtenons toujours la dernière version (ex. :
alpine:latest).
2.4.3 – Démarrer un conteneur (instance d’image) : docker run ID
docker run 47e12946765b
________________________________________
/ No group of professionals meets except \
| to conspire against the public at |
| large. |
\ -- Mark Twain /
----------------------------------------
\ ^__^
\ (oo)\_______
(__)\ )\/\
||----w |
|| ||
Un autre exemple:
$ docker run -e MESSAGE="Bonjour le monde!" alainboudreault/momo-dit
-----------------------------------------------------
Momo dit: Bonjour le monde!
-----------------------------------------------------
2.4.4 – Effacer un conteneur : docker rm ID
# 1 - Identifier le conteneur
$ docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
a27294467a25 47e12946765b "/entrypoint.sh" About a minute ago Exited (0) About a minute ago elegant_gauss
# 2 - Effacer le conteneur
$ docker rm a27294467a25
2.4.5 – Effacer une image : docker rmi ID
# 1 - Obtenir l'image ID
$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
...
lherrera/cowsay latest 47e12946765b 4 years ago 186MB
# 2 - Effacer l'image
$ docker rmi 47e12946765b
Untagged: lherrera/cowsay:latest
...
Deleted: sha256:47e12946765b355fb29cdd14f54e78a05d24cb5d68afc1e0e92cd4a0243a1b1a
...
💡Note : S’il existe des instances ‘conteneurs’ de cette image, il faudra effacer les conteneurs avant ou bien utiliser l’option
-fpour forcer la suppression de l’image.
2.5 – Redémarrer un conteneur : docker restart ID
# Voici un conteneur terminé:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
d09c5b00adca hello-world "/hello" 50 minutes ago Exited (0) 50 minutes ago charming_mcnulty
# Il peut-être redémarré à partir de son ID
$docker restart d09c5b00adca$
# Ou, en utilisant le nom du conteneur:
$ docker restart charming_mcnulty
2.6 – Démarrer un conteneur en mode terminal (-t) interactif (-i) : docker run -it image
$ docker run -it alpine
/ # ls
bin dev etc home lib media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var
/ #
💡Note : la commande
exitva quitter et terminer le conteneur.
2.7 – S’attacher à un conteneur en cours d’exécution : docker attach ID
Pour se connecter à un conteneur démarré en arrière-plan (-it -d), utilisez docker attach ID/OU_NOM.
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
c8026675b9b7 alpine "/bin/sh" About an hour ago Up About an hour intelligent_noether
$ docker attach intelligent_noether
/ # pwd
/
/ # mkdir 420-4C4
/ # cd 420-4C4/
/420-4C4 # touch je-suis-passé-par-ici.txt
/420-4C4 # exit
$
💡Note : La commande
exita provoqué l’arrêt du conteneur.
2.8 – Redémarrer le conteneur précédent : docker restart ID
$ docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
...
c8026675b9b7 alpine "/bin/sh" 2 hours ago Exited (0) 3 minutes ago intelligent_noether
$ docker restart c8
$ docker attach c8
/ # ls -l
total 60
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 25 18:44 420-4C4
...
💡Note : Il n’est pas nécessaire de fournir tout le numéro d’ID dans une commande. Seulement un nombre suffisant de caractères pour rendre l’ID unique.
2.9 – Quitter un conteneur sans provoquer son arrêt : Séquence CTRL P + Q
# CTRL P + Q - permet de quitter sans arrêter le conteneur
/ # read escape sequence
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
c8026675b9b7 alpine "/bin/sh" 2 hours ago Up 3 minutes intelligent_noether
$
2.10 – Arrêter un conteneur : docker stop ID
$ docker stop c8
c8
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
$
2.11 – Nommer un conteneur : docker run --name
$ docker run -it -d --name monAlpine alpine
ce5bde565bfa21f9b3d4f0cf8dc386cfe193c6dabbcc25a676371b51a32ec7c3
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
ce5bde565bfa alpine "/bin/sh" 7 seconds ago Up 6 seconds monAlpine
$ docker attach monAlpine
/ # CTRL P+Q
2.12 – Renommer un conteneur : docker rename nom/ID nouveauNom
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
ce5bde565bfa alpine "/bin/sh" 7 seconds ago Up 6 seconds monAlpine
$ docker rename monAlpine test
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
ce5bde565bfa alpine "/bin/sh" 4 minutes ago Up 4 minutes test
2.13 – Effacer tous les conteneurs et toutes les images
Voici comment réinitialiser à zéro votre installation de docker :
🛑 DANGER : CETTE COMMANDE EFFACE AUSSI LES IMAGES DE MINIKUBE***
Commande pour Linux/macOS :
docker container stop $(docker container ls -aq) && docker system prune -af --volumes
Commande pour PowerShell :
docker container stop $(docker container ls -aq) ; docker system prune -af --volumes
3 – Notions de port IP
Plusieurs images offrent des services via le protocol TCP/IP. Par défaut, le réseau du conteneur est isolé, mais il est possible d’établir un lien (BIND) entre le réseau du conteneur et l’ordinateur hôte.
3.1 – Obtenir l’image du serveur web nginx
Téléchargement de l’image :
$ docker pull nginx
...
Status: Downloaded newer image for nginx:latest
docker.io/library/nginx:latest
3.2 – Créer un conteneur avec un lien sur le port IP 80 : docker run -p P-host:P-conteneur
Lancer le serveur Web sur le port 8080 de l’ordinateur hôte :
$ docker run -it -d -p 8080:80 --name monServeurWeb nginx
eb66bdef2f73caf6ed04e17f132d613a84f9fa15163b074d27fc3a93cbc4c4b3
# Afficher les conteneurs actifs
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
eb66bdef2f73 nginx "/docker-entrypoint.…" 39 seconds ago Up 38 seconds 0.0.0.0:8080->80/tcp monServeurWeb
3.3 – Vérifier le fonctionnement du serveur web : localhost:8080
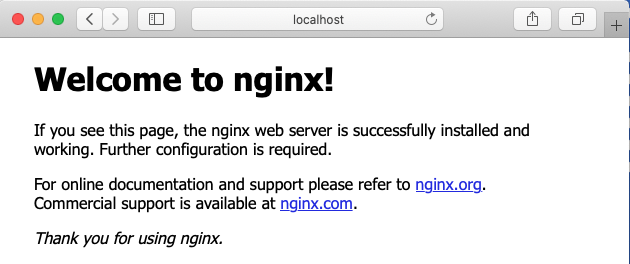
3.4 – Consultation de la documentation de l’image ‘nginx’
https://hub.docker.com/_/nginx
Le répertoire racine du site web est localisé dans :
/usr/share/nginx/html
3.5 – Modifier le contenu : docker exec
# 1 - Connexion au shell du conteneur nginx
$ docker exec -it monServeurWeb /bin/bash
root@eb66bdef2f73:/# cd /usr/share/nginx/html
root@eb66bdef2f73:/usr/share/nginx/html# ls
50x.html index.html
# 2 - Créer un nouveau document html
$ echo "<center><h1>Mon serveur WEB</h1></center>" > index2.html
# Ou installer nano dans le conteneur:
$ apt update $$ apt install nano -y
# 3 - Tester dans le fureteur
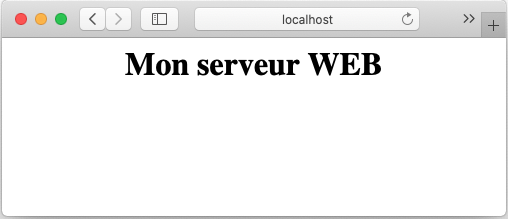
❓Question : Est-ce que quitter le ‘shell’ avec exit va terminer le conteneur?
💡NOTE : la commande
attachva exécuter le point d’entrée. Dans le cas de nginx, cela ne correspond pas à un ‘shell’.

3.6 – Laboratoire
- Créer un conteneur à partir de l’image d’apache disponible sur docker hub.
- Utiliser l’image officielle de ‘The Apache HTTP Server Project’.
- Nommer votre conteneur
WEBSRV. - Utiliser le port local
80pour la connexion au service web. - Remplacer la page d’accueil d’apache par votre propre page personnalisée.
- Tester le nouveau service web.
3.7 – Afficher les statistiques d’utilisation matériel des conteneurs: docker container stats
$ docker container stats
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
CONTAINER ID NAME CPU % MEM USAGE / LIMIT MEM % NET I/O BLOCK I/O PIDS
eb66bdef2f73 monServeurWeb 0.00% 2.098MiB / 1.942GiB 0.11% 41.3kB / 24.1kB 65.5kB / 0B 2
CTRL+C pour quitter
3.8 – Afficher le journal (log) d’un conteneur : docker logs ID|NAME
$ docker logs monServeurWeb
/docker-entrypoint.sh: /docker-entrypoint.d/ is not empty, will attempt to perform configuration
...
/docker-entrypoint.sh: Configuration complete; ready for start up
172.17.0.1 - - [25/Jan/2021:20:41:47 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 612 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_4) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (...)" "-"
...
💡 NOTE: Ajouter l’option ‘-f’ pour un affichage en continu
3.9 – Afficher le détail complet (json) d’un conteneur : docker inspect ID|NAME
$ docker inspect serveur-web
$ docker inspect serveur-web | grep "IPAddress"
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.3",
$ inspect serveur-web | grep "Image"
"Image": "sha256:325b00a35073d9aa1d3df16da8afbbae1ac7d824c505f7490cd5cdbb79d60f6d",
"Image": "nginx:latest",
3.10 – Appliquer un filtre à une commande: docker --filter
$ docker container ls --filter "status=exited"
$ docker run -d --name "toto" --label "app=web-service" --label "environment=production" nginx:latest
$ docker container ls --filter "name=toto"
$ docker container ls --filter "label=environment=production"
# Afficher les conteneurs d'image de type x
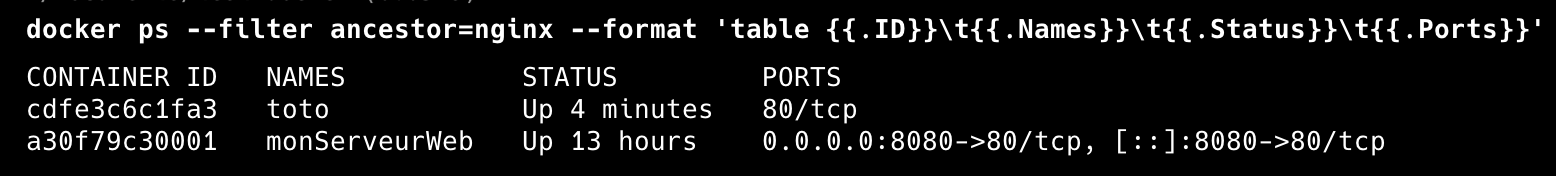
$ docker ps -a --filter ancestor=nginx
# Afficher avec un format personnalisé :
$ docker ps --filter ancestor=nginx --format 'table \t\t\t'
Outils pour Docker
Crédits
Document rédigé par Alain Boudreault © 2021-2026
Version 2025.12.10.1
Site par ve2cuy